There’s no denying that labor costs have a significant impact to any electrical project’s bottom line or that poor planning can risk throwing your project off-timeline and off-budget.
Estimating labor costs is an essential step in the project planning. Most important to accurately estimating labor costs is knowing the approximate hours required for project completion. To determine an estimate of hours you must first determine quantities of materials needed. This will require a thorough review of specifications and drawings.
While calculating materials costs might be as easy as placing a quick call to your preferred supplier, first identifying the proper substrates may be a little trickier. Typically materials are defined within a project’s specifications, however availability, pricing, and project manager preferences may result in alternate options. When subbing out materials, it is important to consider factors beyond raw material cost such as ease of field handling, weight, and labor hours required for installation.
In recent years we’ve seen engineers, electrical contractors and project managers shifting from traditional GRC or PVC materials for their industrial and commercial electrical projects to more readily available and cost effective materials like fiberglass (RTRC) conduit.
The best conduit for your electrical project will depend heavily on the environment of your application. Is it an indoor or outdoor installation? Will the area frequently be wet or exposed to harsh chemicals, as is the case in waste water treatment facilities and chemical plants? Is the environment corrosive or hazardous enough to require XW type or Class 1, Div 2 approved conduit, and will UV exposure, weather, or potential fire exposure need to be considered?
The answer to each of these questions will help determine whether metallic or nonmetallic conduit is right for your project. Some of the more common electrical conduits include:
- PVC SCH 40
- PVC SCH 80
- Galvanized rigid conduit (GRC)
- Fiberglass conduit (RTRC)
It is important to know what material you’ll be working with before you begin to calculate labor costs, as labor installation rates (normal installation hours per 100 feet of material) are specified by the NECA’s Manual of Labor Units by material. A variety of factors influence the estimated time required to install electrical conduit including:
- Ease of field handling
- Product weight
- Support span distances
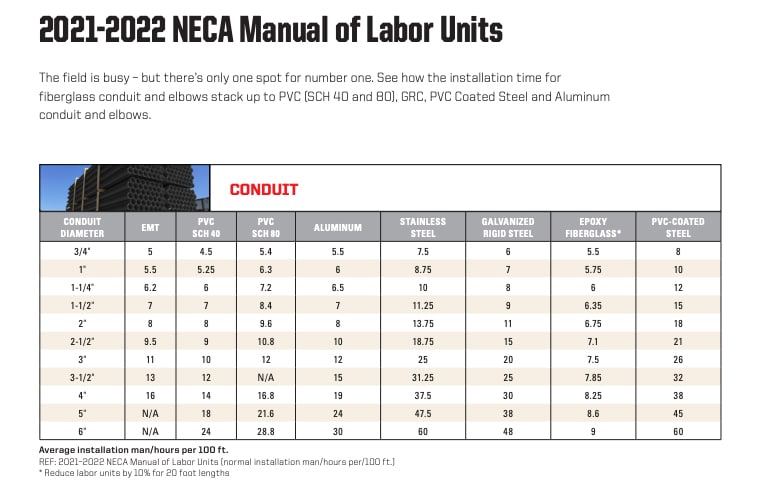
Additional factors that can affect labor pricing for electrical cost estimates include:
- Onsite working conditions
- Project complexity
- Joining systems required
- Productivity levels and experience of crews
- Availability of labor local to the project
- Availability of materials (PVC conduit has faced significant shortages since 2020 which are expected to continue through 2024)
- Code violations or other corrections identified during inspection
Fortunately, several tools exist to make calculating electrical labor costs for conduit much easier, including Champion Fiberglass’ suite of calculators:
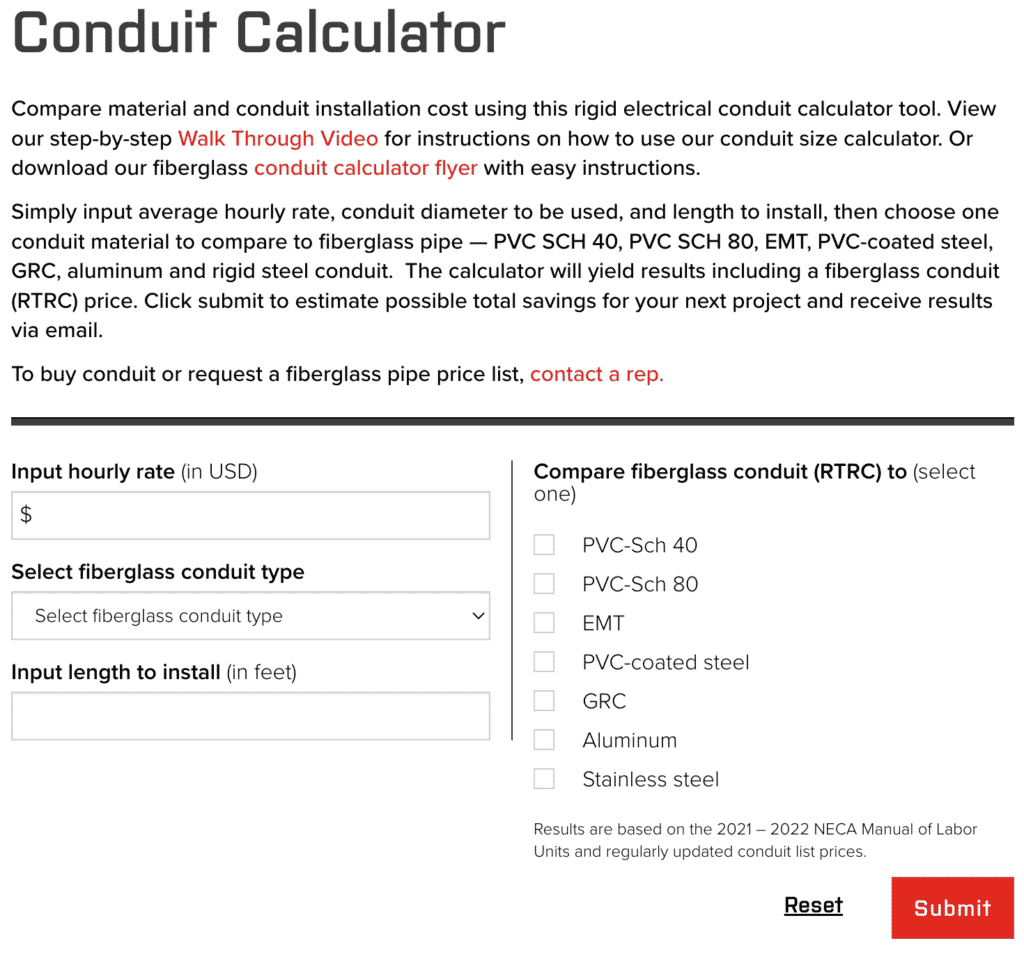
1. Electrical Conduit Calculator, which estimates both materials and labor. You can easily enter the conduit diameter to be used, length to install and average hourly labor rate to compare pricing across common conduit substrates including PVC SCH 40, PVC SCH 80, EMT, PVC-coated steel, GRC, aluminum, rigid steel conduit, and fiberglass (RTRC).
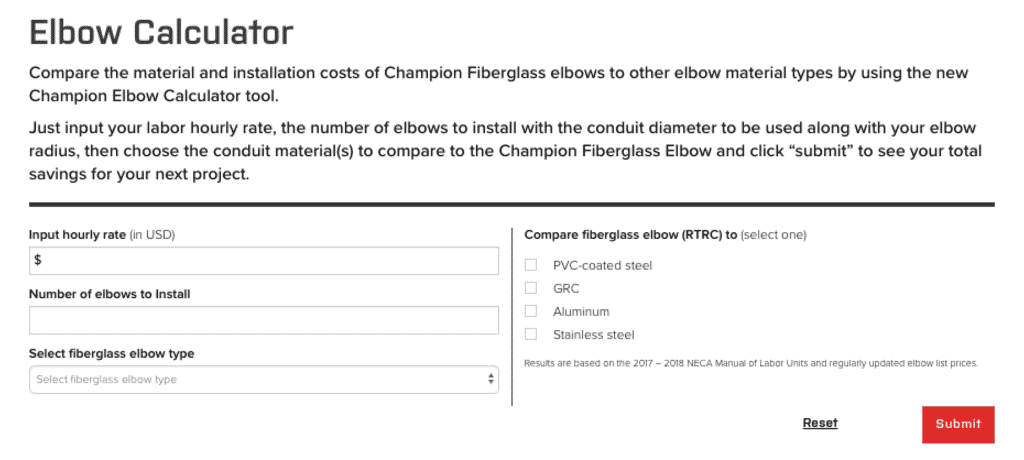
2. Elbows Calculator, which estimates material and labor costs for the elbows required. Once you’ve performed a quantity takeoff you can enter the number of elbows required, as well as conduit diameter and elbow radius to compare estimated project costs for various, common substrates including PVC-coated steel, GRC, aluminum, stainless steel, and fiberglass (RTRC).
For help calculating electrical labor costs of conduit, or for a fiberglass (RTRC) price list, contact your local Rep.










0 nhận xét:
Đăng nhận xét